9-6 Timing – 6 DAYS A WEEK

10 A Ext Gandhi Nagar Jammu, India 18004
Contact us
+91 7006148645 | +91-8491851980
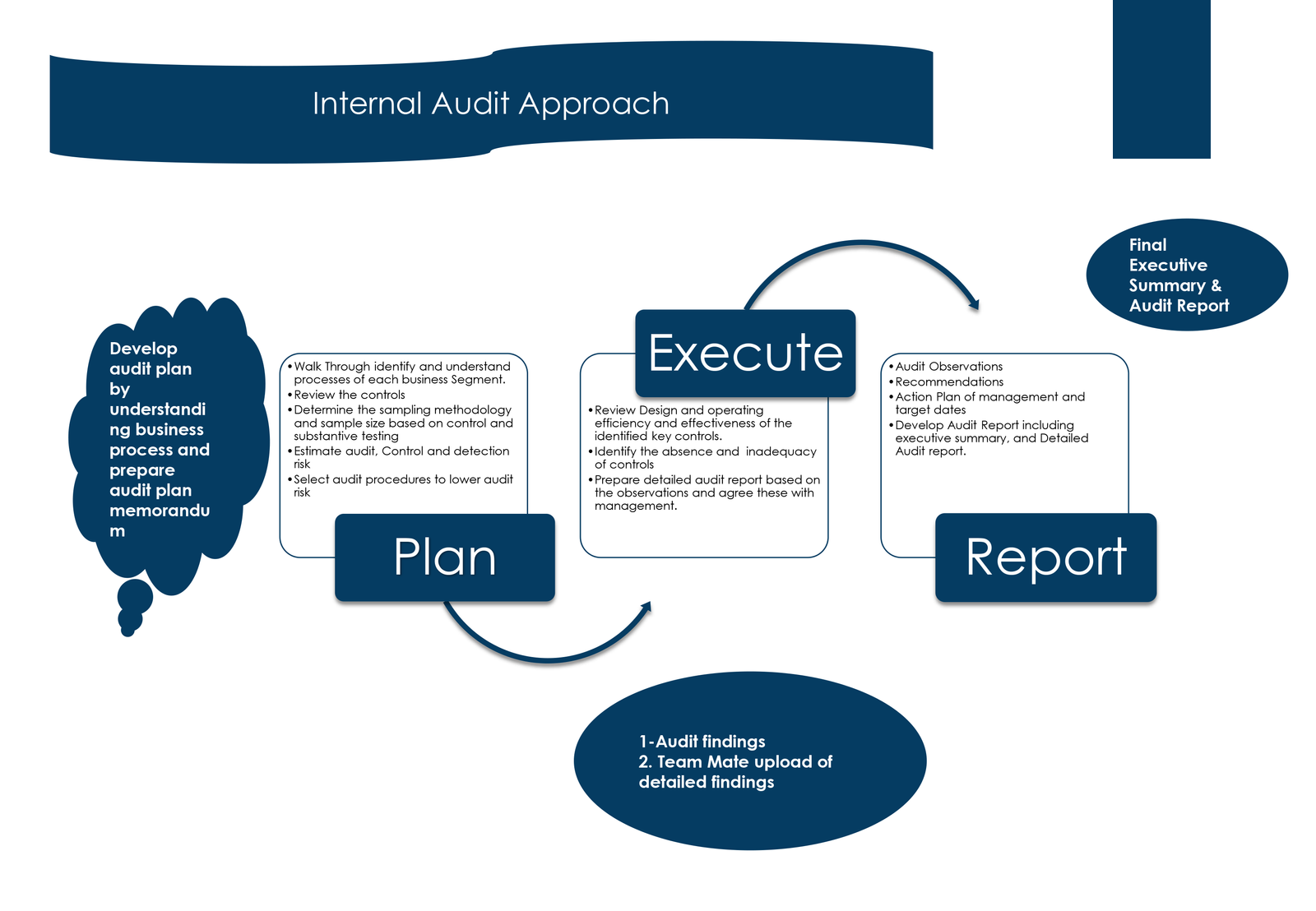
Risk management and internal audit are closely related functions within an organization, each serving distinct but interconnected purposes. Both play critical roles in ensuring the effectiveness of an organization’s governance, risk, and control processes. Let’s explore each of these areas:
Risk Management:
Definition: Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could impact the achievement of organizational objectives.
Process:
Key Components:
Tools and Techniques:
Internal Audit:
Definition: Internal audit is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations.
Roles:
Process:
Key Components:
Tools and Techniques:
Interactions between Risk Management and Internal Audit:
Conclusion: In summary, risk management and internal audit are integral components of a robust governance framework. While risk management focuses on identifying and managing risks, internal audit provides assurance on the effectiveness of risk management processes and contributes to the organization’s overall improvement. The collaboration between these functions helps organizations navigate uncertainties, strengthen internal controls, and achieve their objectives with greater confidence.